About SAML
Security Assertion Markup Language (SAML) is a standard that defines a framework for exchanging security information between online business partners. Based on XML language, it was developed by the Security Services Technical Committee (SSTC) of the standards organization OASIS (the Organization for the Advancement of Structured Information Standards).
SAML offers Single Sign On (SSO) on the web. That way, a user can have restricted access to several different sites by authenticating only once, and these sites do not need to have access to a large amount of data.
CrossKnowledge Learning Suite as Service Provider
Sometimes the client needs to reuse their users database, and has that service provided from one single central service called Identity Provider (IdP), to which one or more Service Providers (SP) can connect to and authenticate their users without having access to the users database (from the IdP). CrossKnowledge Learning Suite (CKLS) can (and is not limited to) integrate as SP to a SAML IdP using SAML 2.0 protocol.
Identity Provider: The Authority in charge of asserting a subject is valid.Service Provider: Some external entity that consumes the assertion services from the authority.
From that approach, the IdP can select which SP can connect to it, how they will share the information, which information will be shared, and what encryption will be applied to that communication. To have that setup, both the SP and the IdP share their metadata.xml file, which describes all the mandatory information to enable them recognising each other as a valid partner.
Set up
CrossKnowledge creates their SP metadata and share that with the client’s IT. The client’s IT imports that metadata adding it as a valid Service Provider description to the Identity Provider service. Once setup on the IdP side, the IdP exports and shared their metadata to CrossKnowledge, which adds the IdP metadata to its SP, completing the handshake between those systems.
For setting up
- via Azure IdP service, please follow this link.
- via OKTA IdP service, please follow this link. For other systems, please consult their own SAML IdP setup documentation.
| Required informations | Description |
|---|---|
| Federation metadata URL | Describes the SAML setup and endpoints (ie : https://FederationMetadata/2007-06/FederationMetadata.xml) |
| Certificate | Used to encrypt data |
| Encrypted SAML-token | A secure way to identify a session between both systems |
| Claim type | What will be shared between those systems (ie : UPN, email address, etc…) |
| NameID Policy | How the SAML assertion will answer for valid assertion challenges (Transient, Persistent, Unspecified or Email address) |
| AudienceRestriction | Add the SP to the list of audience restriction |
How it works
On the SP side, we can configure two different results from a successful assertion, providing real time user provisioning or not.
- If user provisioning is enabled, the user will be created and/or updated on each connection.
- If no provisioning is enabled, the user must exist as the SP side so it can correctly authenticate there.
On provisioning mode, the provisioned data depends on claims provided from the IdP. CKLS can map claims to a learner’s properties.
On a non-provisioning scenario, please consult a CrossKnowledge Integration Engineer for user import options available, whenever needed.
When a user tries to access CKLS as a SP through and IdP, we can have an IdP Initiated or an SP Initiated Assertion request. The former, the user accesses directly the IdP asking for authentication, while the later, the user accesses the SP, which redirects to the IdP for the assertion and expects for the result.
Please see the image below for a summary on that workflow.
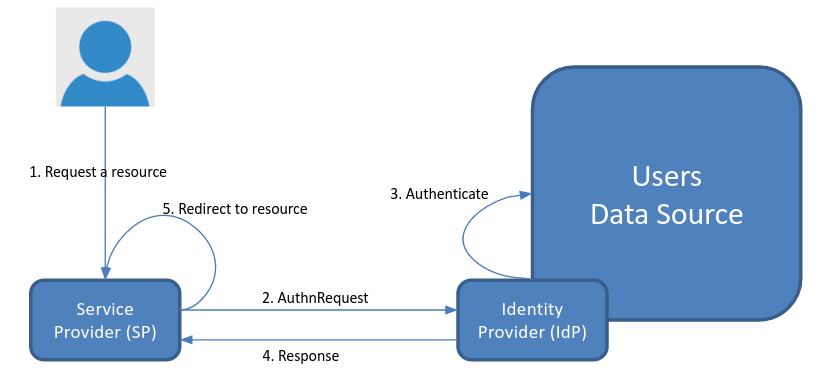
Illustration 1: Authentication workflow on SP initiated mode
For more details on SAML 2.0 protocol, please refer to the OASIS documentation.